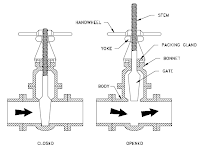
Valves have some basic parts in common irrespective of the
type of valve.These basic parts of valves serve different functions during the
operation of valve.Understanding of basic parts of a valve practically helps plant operators and maintainers to perform their duties in a better way.
Following are the basic parts of a valve.
- Body of valve
- Bonnet of valve
- trim (internal elements) e.g Stem and disc ,seat and sleeve of valve stem
- actuator of valve
- packing of valve
1. Valve Body
Valve body, sometimes called the shell, is the primary
pressure boundary of a valve. It serves as the principal element of a valve
assembly because it is the framework that holds everything of valve together.
Body of valve has to withstand many forces inside the
valve.It is the first pressure boundary of a valve, resists fluid pressure
loads from connecting piping. Body of valve also experiences many forces due to
end connections of a valve. It receives inlet and outlet piping through
threaded, bolted, or welded joints.
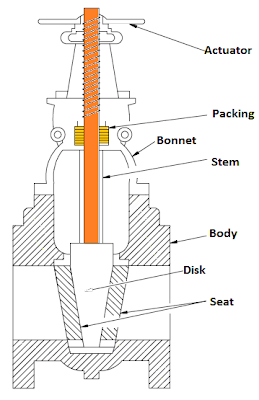 |
| Basic parts of a valve |
The basic form of a valve body ranges from simple block
shapes to highly complex shapes in which the bonnet, a removable piece to make
assembly possible, form part of the pressure resisting body.
2. Valve Bonnet
Valve bonnet is basically the cover for the opening in the
valve body. In some designs, the body
itself is split into two sections that bolt together. Like valve bodies,
bonnets vary in design. Some bonnets function simply as valve covers, while
others support valve internals and accessories such as the steam, disk, and
actuator.
The bonnet of valve is second principal pressure boundary of a valve.
It is cast or forged of the same material as the body and is connected to the
body by a threaded, bolted, or welded joint.
In all cases, the attachment of
the bonnet to the body is considered a pressure boundary. This means that the
welded joint or bolts that connect the bonnet to the body are
pressure-retaining parts.
Bonnets of valves can complicate the manufacture of
valves, increase valve size, represent a significant cost portion of valve
cost.Bonnets of valves are a source for potential leakage.
3. Valve Trim
The internal elements of a valve are collectively called
as valve’s trim. The trim typically
includes a disk, seat, stem, and sleeves needed to guide the stem. A
valve’s performance is determined by the disk and seat interface and the
relation of the disk position to the seat. Contact of disk with seat matters
most when evaluating the performance of valves.Disk to seat contact determines
the presence of leakage from a valve.
Because of trim, basic motions and flow control are
possible. In rotational motion trim designs, the disk slides closely past the
seat to produce a change in flow opening. In linear motion trim design, the
disk lifts perpendicularly away from the seat so that an annular orifice
appears.
4. Valve Disk and Valve
Seat
For a valve having a bonnet, the valve disk is the third
primary principal pressure boundary. The valve disk provides the capability for
permitting and prohibiting fluid flow. With the disk closed, full system
pressure is applied across the disk if the outlet side is depressurized. For
this reason, the disk is a pressure-retaining part. Disks are typically forged
and, in some designs, hard-surfaced to provide good wear characteristics. A
fine surface finish of the seating area of a disk is necessary for good sealing
when the valve is closed. Most valves are named, in part, according to the
design.
The seat or seal rings provide the setting surface for the
disk. In some designs the body is machined to serve as the seating surface and
seal rings are not used. In other designs, forged seal rings are threaded or
welded to the body to provide the seating surface. To improve the
wear-resistance of the seal rings, the surface is often hard-faced by welding
and then machining the contact surface of the seal rings. A fine surface finish
of the seating area is necessary for good sealing when the valve is closed.
5. Valve Stem
Valve stem
connects the actuator and disk for positioning the disk in accordance with requirement. Stems
are typically forged and connected to the disk by threaded or welded joints.
For valve designs requiring stem packing or sealing to prevent leakage, a fine
surface finish of the stem in the area of the seal is necessary. Typically, a
stem is not considered a pressure boundary part.
Two types of valve stems are rising stems and non-rising
stems. These two types of stems are easily
distinguished by observation.
For a rising stem valve, the stem will rise above
the actuator as the valve is opened.
This occurs because the stem is threaded
and mated with the bushing threads of a yoke that is an integral part of, or is
mounted to, the bonnet.
There is no upward stem movement from outside the valve
for a non-rising stem design. For the non-rising stem design, the valve disk is
threaded internally and mates with the stem threads.
6. Valve Actuator
Valve actuator operates the stem and disk assembly. An
actuator may be manually operated hand wheel, manual lever, motor operated,
solenoid operated, pneumatic operated, or hydraulic operated.Valve actuator
basically directs the disc to open ,close or throttle depending upon the type of valve.
7. Valve packing
Valve packing prevent leakage from the space between the
stem and the bonnet. Valve Packing is commonly graphite ring, fibrous material
(such as flax) or another compound (such as Teflon) that forms a seal between
the internal parts of a valve and the outside where the stem extends through
the body.
Valve
packing must be properly compressed to prevent fluid loss and damage to the
valve’s stem. If a valve’s packing is too loose, the valve will leak, which is
a safety hazard. If the packing is too tight, it will impair the movement and
possibly damage the stem.